The thyroid is a small but very important endocrine gland located in the front of the neck. It produces hormones that regulate metabolism, body temperature, heart rate, and many other important body functions. When the thyroid gland is not functioning optimally, we can experience a variety of symptoms: fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, hair loss, or cold intolerance. The most common thyroid diseases are hypothyroidism (too little hormone) and hyperthyroidism (too much hormone). Our daily lifestyle habits and diet directly affect thyroid function. Research shows that the right amount of nutrients and healthy daily habits can help maintain optimal thyroid function. When looking for the most effective ways to support thyroid function, it is important to understand the vital role of vitamins and minerals in the body’s daily processes. Vitamins for immunity also play an important role in maintaining thyroid health.
In this article, you will learn about 11 effective ways to naturally improve thyroid function and maintain it every day, as well as what nutrients are essential for thyroid health and when you should see a doctor.
The Thyroid and Its Importance to Health
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located below the Adam’s apple.
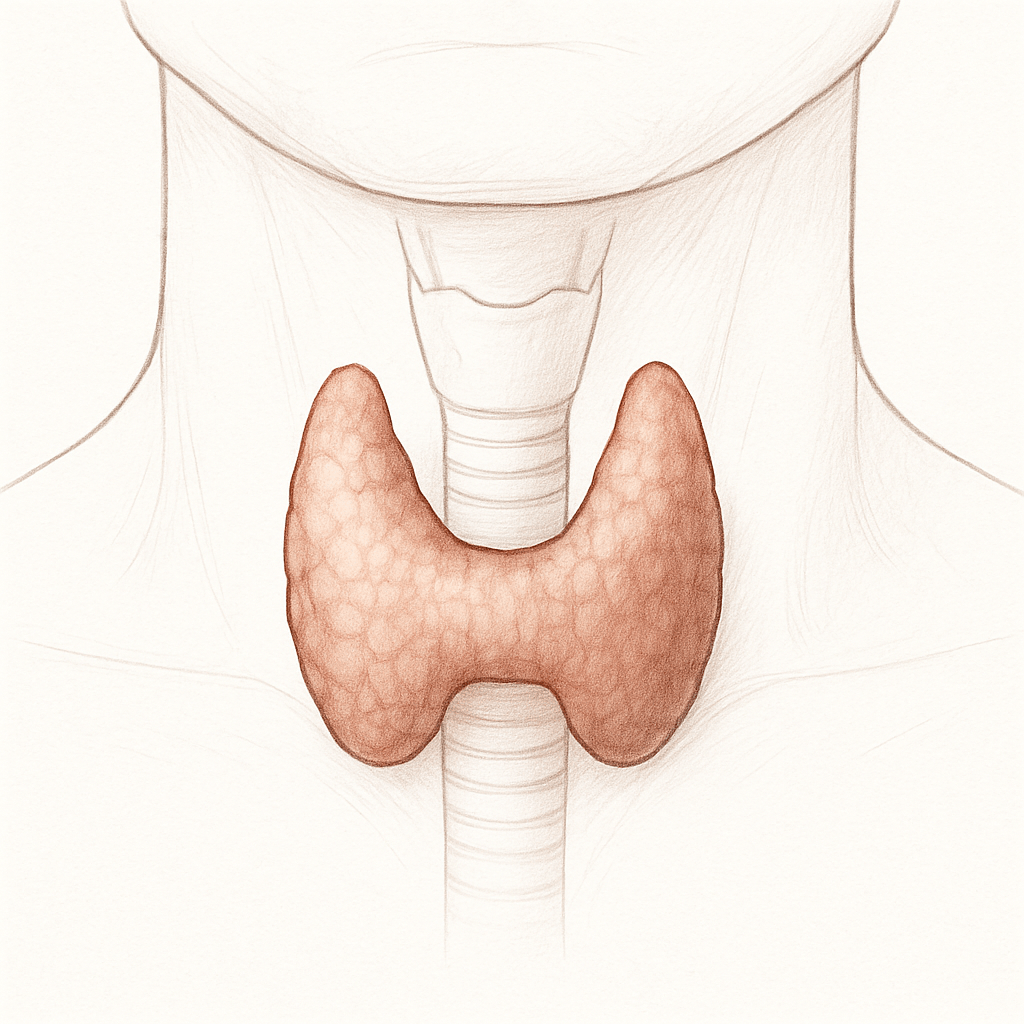
It produces two main hormones, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), which control how the body’s cells use energy. These hormones regulate metabolism, body temperature, heart rate, digestion, and even brain development. Thyroid function is crucial for female fertility and pregnancy.
Thyroid disorders are quite common, with an estimated 5-10% of the population experiencing thyroid problems. Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) is more common in women and older people. Risk factors include autoimmune diseases (especially Hashimoto’s thyroiditis), iodine deficiency or excess, genetic factors, age (over 60), and female gender.
Common thyroid disorders
Hypothyroidism is characterized by fatigue, sensitivity to cold, weight gain, dry skin, hair loss, depression, and constipation. Hyperthyroidism causes anxiety, increased sweating, heat intolerance, weight loss, increased heart rate, and diarrhea. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks thyroid cells, causing inflammation and eventually hypothyroidism.
Regular blood tests are an important part of prevention. Vitamin D levels are one important indicator – Endoca Natural Vitamin D can be a useful supplement to support thyroid health, especially during the winter months when sunlight is lacking.
Key Nutrients for Optimal Thyroid Function
The thyroid gland requires certain nutrients for hormone production and metabolism. Here are the most important ones:
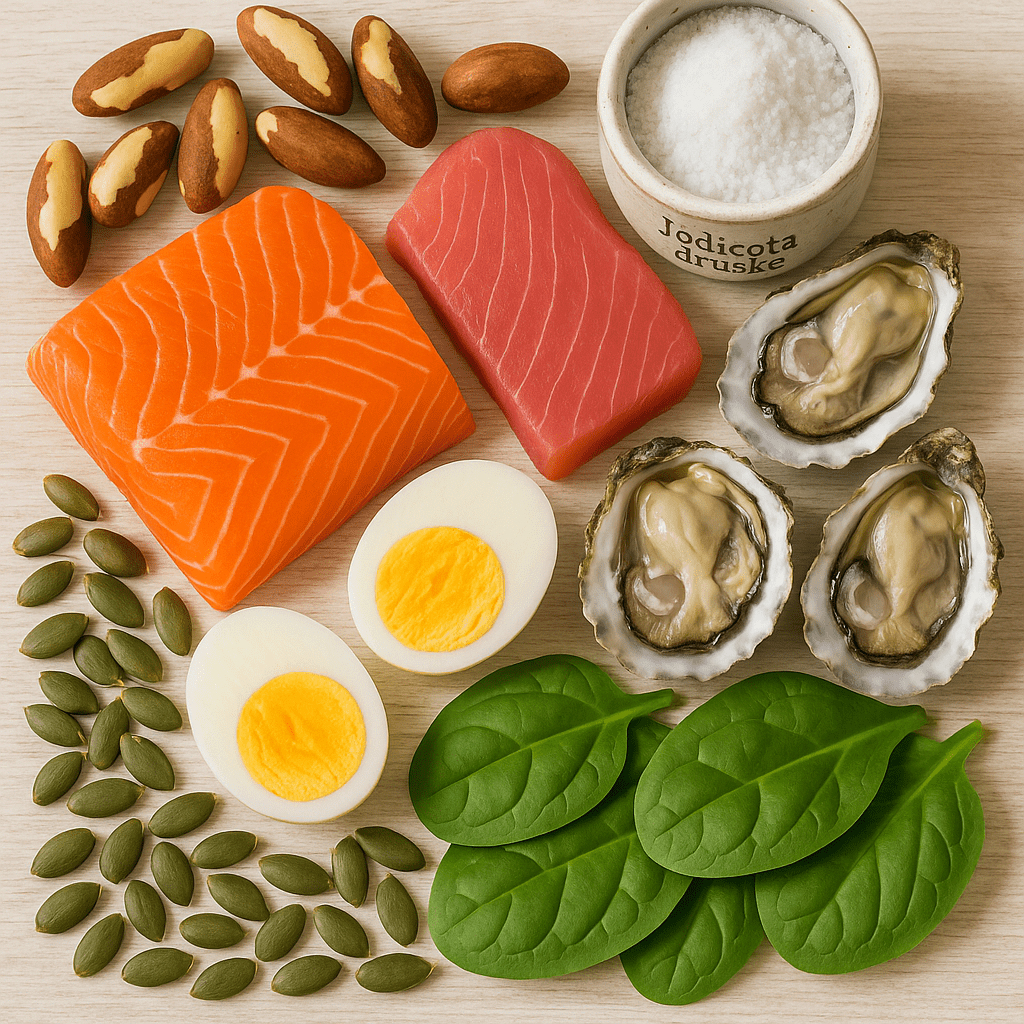

- Iodine – essential for thyroid hormone production. Recommended daily intake: 150 µg for adults. Sources: seafood, iodized salt, dairy products.
- Selenium – involved in the conversion of thyroid hormones and protects against oxidative stress. Recommended daily intake: 55 µg. Sources: Brazil nuts, tuna, eggs.
- Zinc – required for thyroid hormone receptors. Recommended daily intake: 8-11 mg. Sources: pumpkin seeds, beef, oysters.
- Iron – essential for thyroid hormone synthesis. Recommended daily intake: 8-18 mg. Sources: red meat, beans, spinach.
- Vitamin D – regulates the immune system and may reduce the risk of autoimmune thyroid diseases. Recommended daily intake: 600-800 IU. Sources: oily fish, egg yolks, sunlight.
- Vitamin B12 – supports energy levels, especially important in hypothyroidism. Recommended daily intake: 2.4 µg. Sources: meat, fish, dairy products.
It is important to balance the amount of these nutrients – both a deficiency and an excess can cause thyroid disorders. For example, too much iodine can cause both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.
Do nutritional supplements help thyroid health?
Nutritional supplements can only be useful in cases of specific nutrient deficiencies. Before starting any supplements, it is important to consult a doctor and have blood tests done. Scientific studies show that selenium and iodine supplements can be useful in cases of hypothyroidism, but their dosage must be accurate. Zinc helps maintain normal immune system function and is important for thyroid function, so high-quality zinc supplements can be a useful preventive measure, especially for those whose diets lack this mineral.
Food should always be preferred over supplements, but in specific situations (e.g., vegans, seasonal vitamin D deficiency) supplements can be a valuable solution.
11 Best Ways to Improve and Maintain Thyroid Health Every Day
Here are the most effective, science-backed ways to improve and maintain thyroid function every day:
1. Eat selenium-rich foods
Selenium is a mineral essential for the metabolism of thyroid hormones. Studies show that just one Brazil nut a day can provide the recommended amount of selenium. Other good sources include tuna, sardines, eggs, and chicken. Selenium helps protect the thyroid from oxidative stress and is essential for the activity of enzymes that convert T4 to the active form T3.
2. Monitor and balance your iodine intake
Iodine is a key component of thyroid hormones, but it is important to maintain a balance – neither too little nor too much. The best sources of iodine are seafood, iodized salt, and milk and its products. Self-medication with iodine supplements without medical supervision should be avoided, especially if you have autoimmune thyroid diseases.
3. Prioritize sources of zinc and iron
Both of these minerals are essential for the production of thyroid hormones. Sources of zinc include beef, pumpkin seeds, crabs, and oysters. Iron can be obtained from red meat, beans, and spinach. It is especially important for vegetarians and vegans to monitor the levels of these minerals, as iron (non-heme) in plant products is less well absorbed.
4. Include sources of vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased risk of autoimmune thyroid disorders. Natural sources of vitamin D include oily fish (salmon, mackerel), eggs, and mushrooms. In the Lithuanian climate, vitamin D supplements are often needed, especially in winter. It is recommended to regularly check the level of vitamin D in the blood.
5. Consume omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation and may be beneficial in case of autoimmune thyroid diseases. The best sources are oily fish (salmon, sardines, mackerel), flaxseed, chia seeds and walnuts. It is recommended to eat oily fish at least 2-3 times a week.
6. Include protein-rich foods
Protein is important for the transport of thyroid hormones in the blood. High-quality protein sources include eggs, Greek yogurt, fish, poultry, legumes. It is recommended that adults consume about 0.8 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight daily.
7. Maintain gut health
The gut microbiome directly affects thyroid function. Probiotics (kefir, yogurt, fermented vegetables) support healthy gut flora. Fiber (vegetables, fruits, whole grains) feed beneficial bacteria. In addition to diet, natural gut support is also important for thyroid health. Digestive supplements can help improve nutrient absorption, which is especially important for thyroid function.
8. Limit goitrogenic foods or prepare them properly
Some foods (cruciferous vegetables – cabbage, broccoli, turnips) contain goitrogens, which can interfere with iodine absorption. However, you don’t need to completely give them up – heat treatment (boiling, steaming) significantly reduces the amount of goitrogens. It is better to eat these vegetables cooked than raw, especially if you have hypothyroidism.

9. Reduce processed foods and added sugar
Processed foods and added sugar promote inflammation in the body, which can worsen autoimmune thyroid diseases. It is recommended to choose natural, unprocessed products and limit sweets, carbonated drinks, and white bread products.
10. Manage stress
Long-term stress affects cortisol levels, which can negatively affect the production of thyroid hormones. Adaptogenic herbs – ashwagandha (withania somnifera), rosehip (rhodiola rosea) – can help reduce the effects of stress. Regular meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises are also effective in reducing stress.
11. Regular health check-ups and blood tests
Preventive blood tests allow for early detection of thyroid disorders. It is recommended to check the levels of TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), T3, and T4. It is also worth checking the levels of vitamin D, B12, iron, and selenium. Women over 35 with a family history of autoimmune diseases are recommended to have their thyroid checked once a year.
Lifestyle choices and daily habits that support thyroid health
In addition to diet, daily habits also have a significant impact on thyroid function. It is important to pay attention to several key aspects.
Quality sleep is essential for maintaining hormonal balance. Try to sleep 7-8 hours a day and maintain a regular sleep schedule. The blue light from screens before bed can disrupt melatonin production, so it is recommended to avoid electronic devices for at least an hour before bedtime.

Physical activity helps optimize thyroid function, but it’s important to maintain a balance. Moderate-intensity exercise (walking, swimming, yoga) 3-5 times a week is most beneficial. Over-exertion can cause fatigue in hypothyroidism and exacerbate symptoms in hyperthyroidism.
Avoid environmental toxins, especially BPA (bisphenol A), which is found in some plastic containers and cans. Studies show that BPA can disrupt the endocrine system. Also, avoid smoking, which can increase the risk of autoimmune thyroid disease.
Alcohol negatively affects thyroid function and can reduce the effectiveness of treatment, so it should be consumed in moderation or completely avoided, especially if you have thyroid disease. It’s also important to consider drug interactions—some medications can interfere with the absorption of thyroid hormones.
When to See a Doctor: Recognizing Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders often present with nonspecific symptoms that can be mistaken for other medical conditions or simply lifestyle factors. However, there are some clear signs that you should see a doctor.
If you notice several of the following symptoms, it is recommended to consult a doctor:
- Unusual fatigue or lack of energy
- Unexplained weight changes (gain or loss)
- Increased sensitivity to cold or heat
- Heart rhythm disorders (heart rate too fast or too slow)
- Dry skin or increased sweating
- Hair loss or brittleness
- Mood swings, depression or anxiety
- Persistent constipation or diarrhea
- Muscle weakness or joint pain
- In women – menstrual cycle disorders
- Noticable swelling or discomfort in the neck
According to the recommendations of the Lithuanian Ministry of Health, it is recommended that people over the age of 35, especially women, have their thyroid function checked at least once a year, even if there are no symptoms. People with a family history of thyroid disorders or other autoimmune diseases (e.g. type 1 diabetes, celiac disease), should have their thyroid function checked even more frequently.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent more serious complications. Preventive health checkups, including blood tests to assess thyroid function, are an important part of prevention, and high-quality immune vitamins can be an additional step in maintaining overall health.
Conclusion
Thyroid health is a complex phenomenon that depends on many factors, from proper nutrition to stress management and environmental factors. The main elements that help maintain optimal thyroid function are a balanced diet with sufficient iodine, selenium, zinc and vitamin D, regular physical activity, stress management and avoidance of environmental toxins.
The most important thing to remember is that while natural methods can be useful in maintaining thyroid health, they cannot replace medical care if thyroid function is impaired. Regular health check-ups, especially for those at risk, are essential for early detection and effective treatment.
Start with small but consistent changes – include more thyroid-supporting foods in your diet, reduce stress, regulate physical activity and monitor your body’s signs. Consult your doctor before taking any supplements or changing your diet, especially if you already have a thyroid condition or are taking medication.
Frequently Asked Questions
What foods are best for thyroid health?
Priority foods include foods rich in selenium, iodine, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids: Brazil nuts, fish, eggs, and fermented dairy products.
Can I improve thyroid function naturally without medication?
Diet and lifestyle changes can help support thyroid health, but hypothyroidism often requires prescription hormones. Always consult your doctor.
How does stress affect the thyroid?
Chronic stress can disrupt thyroid hormone balance and worsen symptoms. Stress reduction techniques and adaptogenic herbs can help.
Do everyone with thyroid disorders need supplements?
Not everyone. Testing with a doctor is necessary to determine specific deficiencies; supplements should only be taken when needed.
What blood tests should I order to check my thyroid?
Basic tests: TSH, free T4, free T3, and often tests for vitamin D, B12, iron, and selenium.