Vitamin D is often called the “sunshine vitamin” because our bodies produce it when exposed to sunlight. This unique vitamin actually acts like a hormone and is essential for the normal functioning of bones, muscles, and immunity. Unfortunately, in northern countries, including Lithuania, due to its geographical location and long winter months, many people are vitamin D deficient. In order to maintain optimal health, it is important to know the right vitamin D intake and how to achieve it daily.
Children whose bones are still forming, adults who spend a lot of time indoors, older people whose skin produces less vitamin D, and people living in northern climates should pay special attention to their vitamin D levels. In this article, you will learn about the recommended vitamin D intakes for different age groups, how to recognize signs of deficiency, and what are the main sources of this important vitamin. Adequate vitamin D levels in the body are one of the essential elements of strengthening immunity.
Why is vitamin D important? Its functions and benefits
Vitamin D performs many vital functions in our body, and its sufficient level directly affects the general state of health. First of all, this vitamin is necessary for the absorption of calcium and phosphorus in the intestines – minerals necessary for the formation of healthy bones and teeth. Without the right amount of vitamin D, the body cannot effectively use these minerals, even if they are obtained in sufficient quantities from food.
Recent scientific research reveals an even wider health effect of vitamin D:
- strengthens the immune system, helps fight infections and prevent autoimmune diseases;
- ensures normal muscle function and strength, which is especially important for older people;
- participates in regulating mood and can help reduce the risk of depression;
- reduces the risk of chronic diseases, including some forms of cancer;
- supports the cardiovascular system, helps regulate blood pressure.
According to the World Health Organization, more than a billion people worldwide suffer from vitamin D deficiency. In Lithuania, due to its geographical location and limited number of sunny days, especially in the autumn-winter period, maintaining optimal vitamin D levels becomes a real challenge. Therefore, it is important to understand how much of this vitamin is needed daily and how to ensure its sufficient amount in the body.
How much vitamin D is needed daily?
Norms for different age groups
The need for vitamin D varies depending on a person’s age, lifestyle and individual risk factors.
Recommended levels are usually given in international units (IU) or micrograms (μg) – 1 μg is equivalent to 40 IU.
Recommended daily allowances of vitamin D:
- Infants (0-12 months): 400-1000 IU (10-25 μg) per day
- Children (1-18 years): 600-1000 IU (15-25 μg) per day
- Adults (18-65 years): 800-2000 IU (20-50 μg) per day
- People over 65 years: 800-2000 IU (20-50 μg) per day
- Pregnant and nursing mothers: 800-2000 IU (20-50 μg) per day
Lithuanian and European health professionals often recommend higher allowances during the cold season (October-April), when sun exposure is minimal. It is important to note that these are general recommendations and individual needs may vary.
Increased vitamin D levels may be recommended for the following risk groups:
- people with dark skin (melanin reduces the skin’s ability to produce vitamin D);
- those who spend little time outdoors;
- those who regularly use sunscreen;
- those who are overweight or obese (vitamin D accumulates in adipose tissue);
- those with malabsorption syndromes (Crohn’s disease, celiac disease);
- those taking certain medications (e.g. anticonvulsants, steroids).
Vitamin D Testing and Monitoring
Vitamin D levels are measured by measuring the concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) in the blood. According to the latest recommendations:
- Deficiency: less than 30 nmol/L (12 ng/mL)
- Insufficient level: 30-50 nmol/L (12-20 ng/mL)
- Normal level: 50-125 nmol/L (20-50 ng/mL)
- Toxic level: above 250 nmol/L (100 ng/mL)
It is recommended to have a vitamin D test in the spring (March-April), when its levels in the body are lowest. For people in risk groups, doctors may recommend checking vitamin D levels more often. For many people, measuring the concentration of vitamin D in the blood helps to more accurately select the right dose of supplements and avoid overdose.
Signs of Vitamin D Deficiency and Excess
Because vitamin D has so many important functions, a deficiency can manifest itself in a variety of symptoms. Unfortunately, these symptoms are often non-specific and can be attributed to other health problems, so vitamin D deficiency often goes undiagnosed.
Signs of vitamin D deficiency in adults:
Fatigue and lack of energy;
Bone and muscle pain, especially in the back;
- Muscle weakness;
- Depressed mood or symptoms of depression;
- Frequent infections and prolonged recovery;
- Hair loss;
- Slow wound healing;
- Osteomalacia (softening of the bones).
Signs of vitamin D deficiency in children:
- rickets (bone deformities, especially in the legs);
- growth retardation;
- dental problems;
- muscle weakness;
- frequent respiratory infections.
Long-term vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased risk of osteoporosis, some cancers, heart disease, autoimmune diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Although vitamin D deficiency is a more common problem, overdose can also cause serious health problems. Excess vitamin D usually occurs only from taking too much of a supplement (not from food or sun exposure).
Symptoms of vitamin D overdose include:
- nausea and vomiting;
- confusion and disorientation;
- increased thirst and frequent urination;
- loss of appetite and weight loss;
- kidney stone formation;
- hypercalcemia (high blood calcium levels);
- heart rhythm disorders;
- bone pain.
The upper safe dose of vitamin D for adults is generally considered to be 4,000 IU per day, although doctors may prescribe higher doses for short periods of time for some individuals, especially those with a deficiency. It is always important to follow the recommendations of a health professional and not exceed the prescribed doses without supervision.
When taking care of bone health, remember that vitamin D is only one of many important components. You can find more information about vitamins and minerals that help maintain healthy bones and joints on specialized websites.
How to get enough vitamin D? Sources and practical tips
Vitamin D is unique in that we can get it in three main ways: through sunlight, food and supplements. To achieve the recommended vitamin D intake, it is often necessary to use all of these sources, especially in northern countries.
Sunlight
The sun’s UVB rays are the main natural source of vitamin D. When these rays reach the skin, a chemical reaction occurs in it, during which vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is produced. However, the production of vitamin D through the skin is affected by many factors:
- Geographical location: In the geographical latitude of Lithuania, the intensity of UVB rays is insufficient for effective vitamin D production from October to April.
Time of year and time of day: In summer, vitamin D production is most effective from 10 a.m. to 3 p.m. - Skin color: Darker skin produces less vitamin D than fair skin.
- Age: Older people’s skin produces less vitamin D.
- Sunscreen: SPF 15 sunscreen reduces vitamin D production by 99%.
To get the optimal amount of vitamin D, it is recommended to be in the sun without sunscreen (face, arms and legs exposed) for 15-30 minutes 2-3 times a week during the warm season. However, it is important not to overheat and avoid burns.
Food
Unfortunately, vitamin D is naturally found in few foods. The best food sources are:
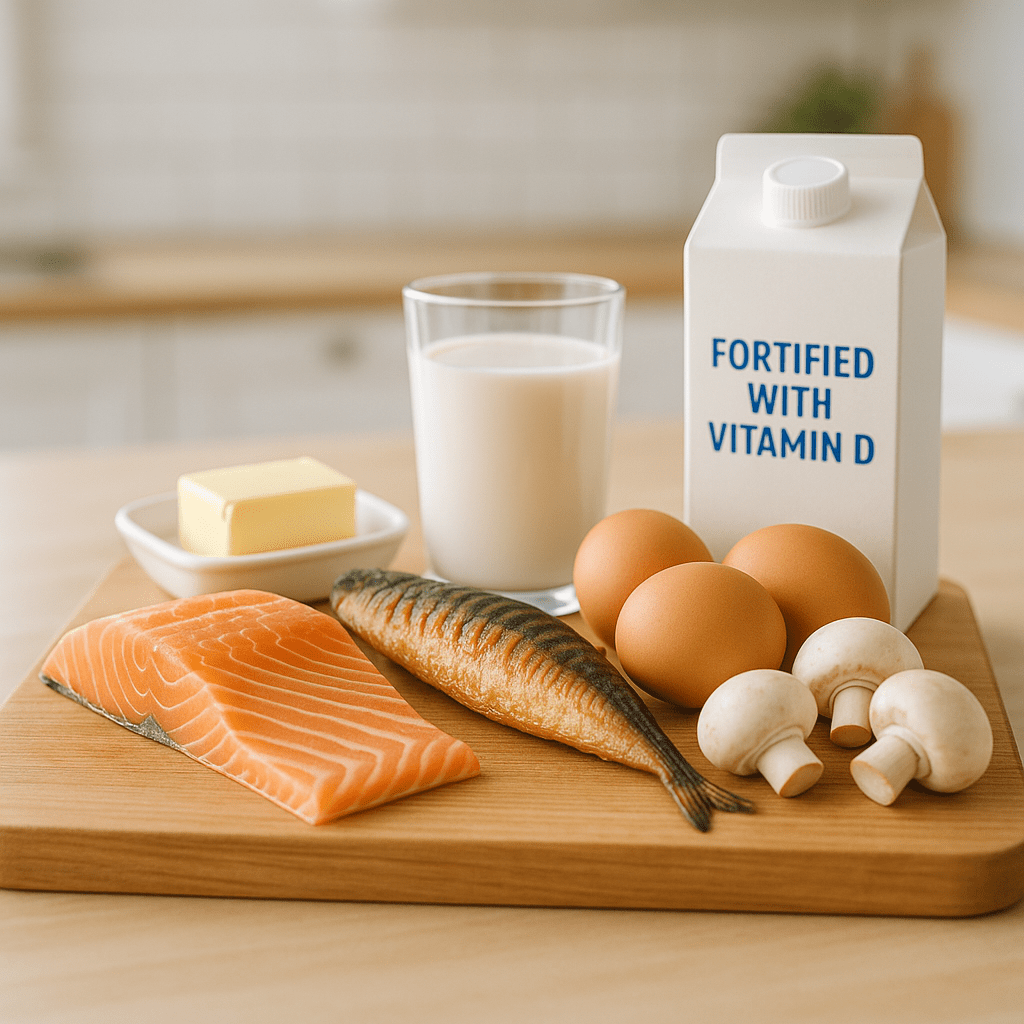

- Fatty fish: salmon, mackerel, herring, tuna (100 g of salmon contains about 400-500 IU of vitamin D).
- Fish oil: a traditional but effective source (1 tablespoon contains about 400-500 IU).
- Egg yolks: one egg contains about 40 IU of vitamin D.
- Liver: beef liver contains a small amount of vitamin D (about 50 IU per 100 g).
- Fortified products: some dairy products, orange juice, cereals and plant-based milk substitutes are fortified with vitamin D.
Even when eating these products regularly, it is difficult to reach the recommended vitamin D intake through food alone. For example, to get 800 IU, you would need to eat about 200 g of salmon daily.
Supplements
For these reasons, vitamin D supplements are becoming a necessity for many people, especially in northern countries. When choosing a supplement, it is important to pay attention to several aspects:
- Form: Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is more effective than D2 (ergocalciferol).
- Dose: The amount of vitamin D in supplements can range from 400 IU to 5,000 IU or more. Choose a dose that meets your needs and your doctor’s recommendations.
- Timing: Vitamin D is best taken with fatty foods, as it is a fat-soluble vitamin.
- Combination: Vitamin D supplements are often combined with vitamin K2 and magnesium, which help to optimally absorb and distribute calcium in the body.
During the cold season (October-April), most adult Lithuanians are recommended to take 1,000-2,000 IU of vitamin D supplements daily. However, the specific dose should be selected individually, taking into account the level of vitamin D in the blood, lifestyle and health status.
For those who want to take care of their immunity and ensure sufficient vitamin D levels, it is worth investigating reliable vitamin D supplements for daily use that are manufactured to the highest quality standards.
Conclusion
Sufficient vitamin D is essential for our health, from bone strength to immune function. In the Lithuanian climate, achieving optimal vitamin D levels is a challenge that often requires a comprehensive approach – combining sunbathing in the warm season, a vitamin D-rich diet and supplements, especially in the autumn-winter period.
It is important to know your individual needs, which depend on age, lifestyle, skin type and other factors. Regularly checking your vitamin D levels in your blood helps ensure that you are neither deficient nor deficient, and allows you to accurately adjust the dose of supplements.
Remember that vitamin D is only one, albeit very important, element of health. A balanced diet, regular physical activity and an overall healthy lifestyle are no less important components of health. Always consult a doctor or nutritionist before taking any supplements, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Take care of your health with the right amount of vitamin D and feel the difference in your energy levels, immunity and overall well-being. Learn more about natural immunity boosting and take care of yourself smartly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the optimal daily intake of vitamin D for adults and children?
The optimal amount of vitamin D varies by age and individual needs, but general recommendations are: 400-600 IU for infants, 600-1000 IU for children, and 800-2000 IU for adults. Always consult your doctor for personal recommendations.
How do I know if I am deficient in vitamin D?
Common symptoms include fatigue, bone or muscle pain, frequent infections, or mood swings. The most accurate way to check vitamin D levels is with a 25(OH)D blood test.
Can I get too much vitamin D?
Yes, taking too many supplements can cause toxicity, leading to high calcium levels in the blood and related health problems. Do not take large doses without medical supervision.
Is sunlight enough to meet our vitamin D needs?
For most people, regular sun exposure can help, but in northern climates or for people with limited sun exposure, dietary sources and supplements may be necessary.
What are the best foods for vitamin D?
Oily fish (such as salmon and mackerel), egg yolks, liver, and fortified foods are the richest natural sources of vitamin D.