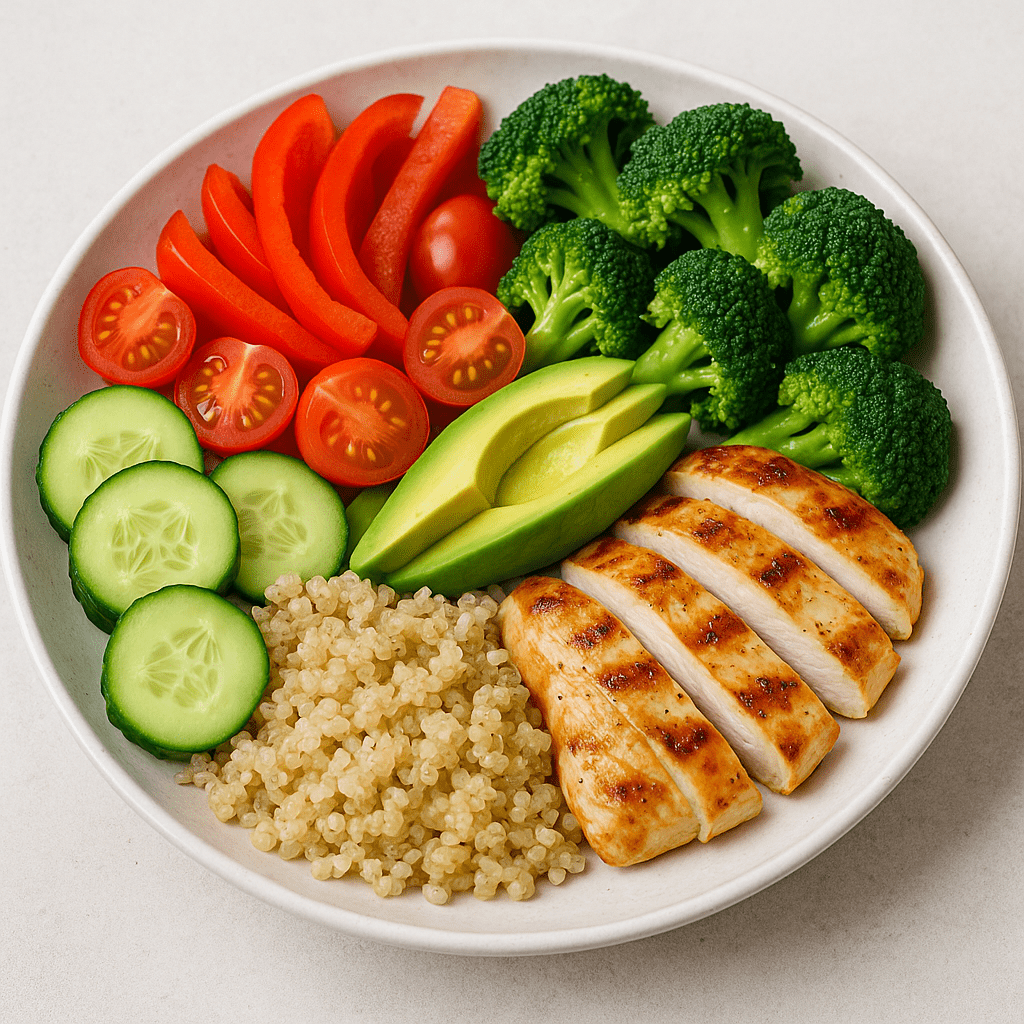In today’s world, where there is a lot of conflicting information about nutrition, balanced food is becoming an essential component of a healthy lifestyle. Balanced nutrition is not only a choice of individual foods, but also a daily nutrition structure that ensures the intake of all necessary nutrients into the body. Such nutrition is important for all age groups and different lifestyles – both those who play sports, and those who do mental work or are preparing for parenthood.
Specialists from the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences emphasize that a properly balanced diet not only helps maintain normal body weight, but also has a direct impact on energy levels, mood and long-term health. Daily selection of the right foods can significantly reduce the risk of chronic diseases and improve the quality of life. In this article, you will learn about the basic rules of a balanced diet, the necessary nutrients and practical advice on how to improve your eating habits. You will also find a daily nutrition plan that will help you more easily apply this knowledge in everyday life.
The balance of nutrients in the body is a key factor in determining our health. Various supplements, such as chlorella, can be a great additional source of antioxidants and other valuable substances in your daily diet.
What is a balanced diet?
A balanced diet is a way of eating that ensures that the body receives all the necessary nutrients in the right proportions. It is not a temporary diet or a strict regime – it is a long-term strategy that helps ensure optimal health and well-being.
According to the recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Lithuania, a balanced diet should consist of various food groups: vegetables, fruits, whole grains, healthy fats, proteins and dairy products. These food groups provide the body with essential vitamins, minerals and other nutrients.
It is important to pay attention to the distribution of products on the plate: half of the plate should consist of vegetables and fruits, a quarter of protein products, and another quarter of grain products.
This distribution helps ensure the right balance of nutrients and energy levels.
A balanced diet differs from a simply “healthy” diet in that it emphasizes not only the choice of healthy foods, but also their proportion and variety. For example, although avocado is considered a healthy food, eating it alone would be unbalanced because it would lack other important nutrients.
The body needs a variety of energy, vitamins, and minerals to function properly. The energy we get from food is measured in calories, and each person’s needs vary depending on age, gender, physical activity, and other factors. On average, women need about 2,000 calories per day and men need about 2,500, but these numbers can vary.
Basic rules for a balanced diet
In order to follow a balanced diet, it is important to follow certain basic rules. These rules are not complicated, but following them can have a significant impact on your health and well-being.
First of all, it is important to eat regularly – at least 3-5 times a day, in small portions. This helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and avoid overeating. It is recommended to have breakfast within the first hour after waking up, and eat the last meal of the day at least 3 hours before bedtime.
Secondly, you should avoid highly processed foods that are rich in added sugar, salt and unhealthy fats. Instead, prioritize fresh, seasonal products. Lithuanian nutritionists recommend that plant-based products make up the majority of your diet – at least 400 g of vegetables and fruits per day.
Thirdly, it is important to drink enough water – at least 1.5-2 liters per day. Water helps maintain metabolism, removes toxins and helps maintain skin elasticity.
Fourth, you should diversify your diet – vegetables and fruits of different colors, various grains, legumes, nuts, seeds and animal products provide a wide range of nutrients. The more diverse your diet, the greater the likelihood of getting all the necessary nutrients.
Fifth, it is important to pay attention to portion size and eating speed. Eating slowly allows you to feel full faster and avoid overeating.
Looking for a more detailed nutrition plan tailored to your individual needs? On our website you will find detailed, professionally prepared plans that will help you achieve your health and well-being goals.
Portion control
Portion control is a key aspect of a balanced diet. Often, the problem is not what we eat, but how much we eat. Even healthy foods, consumed in excessive amounts, can become an obstacle to achieving health or weight management goals.
A simple way to control portions is to use your hands as a measuring device. The palm of your hand can be used to measure a portion of protein (about 85-100 g), a fist for a portion of vegetables or grains, and your thumb for a portion of fat (such as olive oil or butter). This method is convenient because the size of your hand is usually proportional to your body.
Another effective method is to use smaller plates and bowls. Studies show that people who use smaller plates eat smaller portions, but feel just as full.
Eating regularly also helps with portion control – when you eat every 3-4 hours, you are less likely to be very hungry and overeat.
It is important to learn to recognize true hunger and fullness. Before you reach for more food, pause and ask yourself if you are really still hungry. Often, eating is an automatic action that is not related to physiological needs.
Portion control is a habit that takes time to form. However, over time, it becomes a natural part of eating and helps ensure that your body gets the amount of food it needs – neither too much nor too little.
Nutrients: proteins, fats, carbohydrates and fiber
A balanced diet is based on the proper distribution of the main nutrients – proteins, fats and carbohydrates – without forgetting the importance of dietary fiber. Each of these substances performs specific functions in the body and is necessary for its normal functioning.
Proteins are essential for the construction and renewal of cells. They are the basis of muscles, skin, hair and nails, and are also involved in the production of enzymes and hormones. In Lithuania, popular sources of protein are lean meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes (beans, lentils, peas) and nuts. It is recommended that proteins account for about 15-30% of total calories, or about 0.8-1.6 g of protein per kilogram of body weight per day, depending on physical activity.
Fats are often mistakenly considered unhealthy, but they are essential for the body’s functioning – they help absorb vitamins A, D, E and K, provide energy, maintain hormonal balance, protect organs and help maintain normal body temperature. Healthy sources of fat include olive oil, avocados, nuts, seeds and oily fish (salmon, mackerel). Fats should make up about 25-35% of total calories, but it is important to choose unsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, limiting the amount of saturated and trans fats.
Carbohydrates are the main source of energy, especially for the brain and muscles. They are divided into simple (sugar, honey) and complex (grains, legumes, vegetables). Popular sources of carbohydrates in Lithuania are rye bread, buckwheat, oats, barley, potatoes and various vegetables and fruits. It is recommended that carbohydrates make up about 45-65% of total calories, with priority given to complex carbohydrate sources.
Dietary fiber, although not considered an essential nutrient, is an indispensable part of a balanced diet. It improves digestion, helps maintain normal cholesterol and blood sugar levels, and provides a longer feeling of satiety. Fiber is especially important for intestinal health, as it nourishes good intestinal bacteria and promotes their growth. Lithuania is rich in fiber sources: grain products (especially whole grain), legumes, vegetables, fruits, nuts and seeds. It is recommended to consume at least 25-30 g of fiber daily.
Vitamins and minerals, although needed in smaller quantities, are also essential for the body. They participate in various biochemical reactions and ensure the normal functioning of the body. Vitamin and mineral deficiencies can cause various health problems, so it is important to ensure their diversity in the diet.
To ensure the right balance of nutrients, it is recommended to follow this distribution: about 45-65% of calories should come from carbohydrates, 15-30% from protein and 25-35% from fat. However, these figures can be adjusted depending on individual needs, physical activity level and health status.
Foods That Are Good for You and Foods That Should Be Avoided
To maintain a balanced diet, it is important to know which foods should be the basis of our diet and which foods should be limited. This knowledge helps us make informed decisions when shopping and preparing food.
Foods that are good for you and are worth including in your daily diet are leafy greens (cabbage, spinach, kale), which are rich in vitamins, minerals and antioxidants. Colorful vegetables and fruits (carrots, tomatoes, blueberries, raspberries) are also excellent sources of vitamins, minerals and phytonutrients. Whole grains (rye bread, buckwheat, brown rice, oats) provide complex carbohydrates, fibre and B vitamins.
Lean protein-rich foods—poultry (especially breast), fish (especially fatty ones like salmon or mackerel), eggs, legumes (beans, lentils, peas), and low-fat dairy and its products—are essential for muscle growth and repair. Healthy fats, found in nuts, seeds, olive oil, and avocados, help absorb fat-soluble vitamins and support brain function.
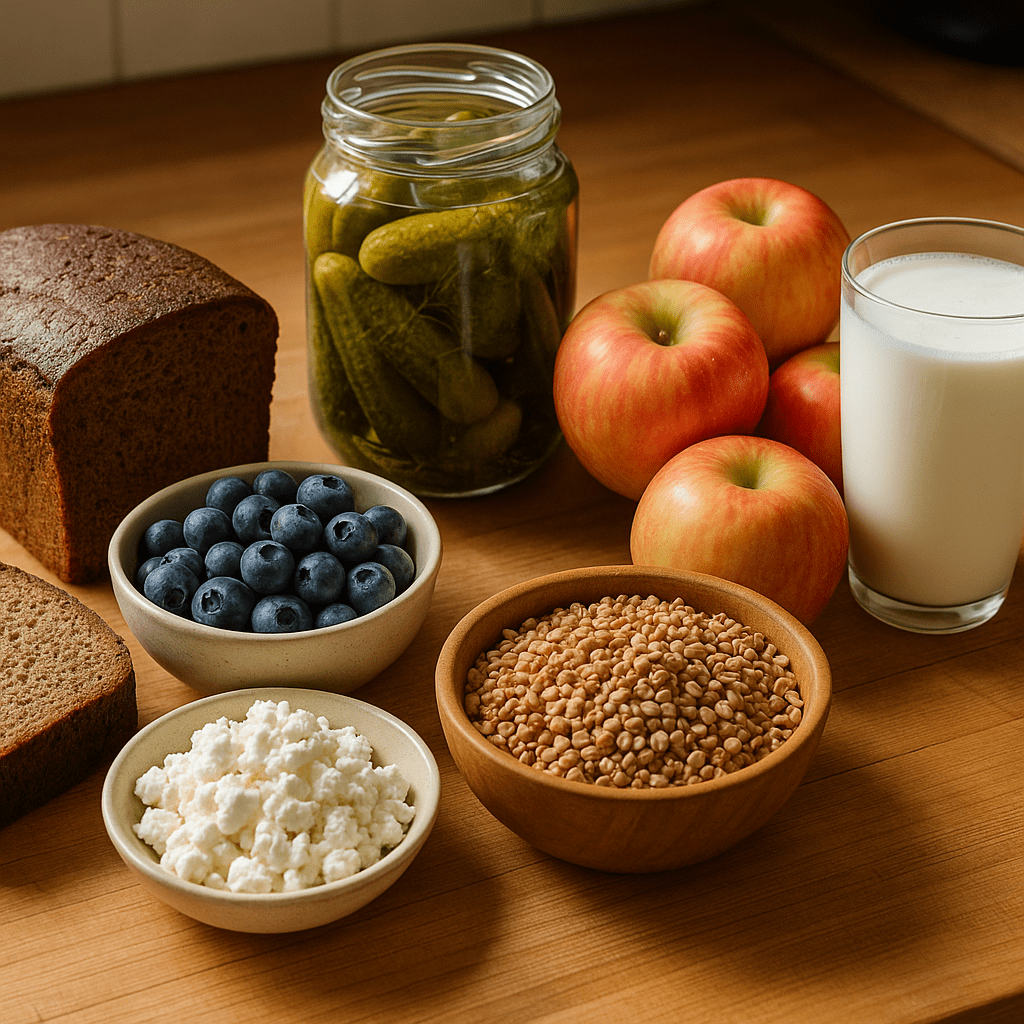
Lithuanian cuisine is rich in healthy foods: sauerkraut and cucumbers, buckwheat, rye bread, apples, fresh berries, cottage cheese, and sour milk.
These traditional products are a great addition to a balanced diet and are easily accessible to everyone.
On the other hand, there are products that should be limited in consumption. These include products with a high sugar content (sweets, cakes, cookies, carbonated drinks), processed meats (sausages, sausages, smoked meats), white flour products (white bread, buns), snacks with a high salt content (chips, salty nuts) and fast food. These products are often high in calories, but they lack nutrients, and they can contribute to weight gain and the risk of various chronic diseases.
In the case of a vegetarian diet, it is especially important to ensure sufficient protein, iron, zinc and vitamin B12. The main sources of protein for vegetarians are legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas), soy and its products (tofu, tempeh), eggs and dairy products (if consumed). Iron can be obtained from dark leafy vegetables, herbs (parsley, dill), legumes and dried fruits, but its absorption without animal products is poorer, so it is worth combining these products with foods rich in vitamin C (citrus fruits, paprika) – this improves iron absorption. Sources of zinc – legumes, seeds, nuts, whole grains. Vitamin B12 is naturally found only in animal products, so vegans often need supplements or B12-enriched products.
A vegetarian diet can be completely balanced if properly planned. It is important to ensure food variety and pay attention to products that can compensate for nutrients not obtained from meat.
Do you want to supplement your diet and ensure the necessary amount of nutrients? Our specially designed fiber supplement “Gut Balance” will help maintain an optimal digestive system and provide energy for the whole day.
Practical tips and a sample daily meal plan
The principles of a balanced diet are easier to apply when we have a clear plan and practical advice. In this section, you will find specific steps on how to implement the rules of a healthy diet in everyday life.
The first step towards a balanced diet is thoughtful shopping. Before going to the store, make a shopping list based on the planned meals for the week.
This will help you avoid impulse purchases and ensure that you have all the healthy products you need at home. Try to shop when you are not hungry, which will reduce the temptation to buy unhealthy snacks.
Meal prepping is a great way to ensure that you have healthy meals ready for workdays. You can spend a few hours on Sunday preparing the main meals for the week, or at least chopping vegetables, cooking grains, or marinating protein sources. This will save time on workdays and reduce the temptation to order fast food.
For busy people, it is important to have healthy, quick-to-prepare snacks – fruit, nuts, yogurt, hard-boiled eggs, or hummus with vegetables. This will help prevent hunger pangs and unhealthy snacks.
Eating habits are formed gradually, so you should not strive for drastic changes in one day. Start with small changes – replace white bread with rye bread, add more vegetables to your diet, reduce the amount of sugar in your coffee. Small steps eventually lead to big changes.
Here is a sample daily meal plan that meets the principles of a balanced diet:
Breakfast (7:00-8:00):
- oatmeal with unsweetened milk or a plant-based drink
- fresh or frozen berries
- handful of walnuts or seeds
- unsweetened herbal tea or coffee with a minimum amount of milk
Lunch (10:00-11:00):
- an apple and a small amount of almonds
- or Greek yogurt with fresh berries
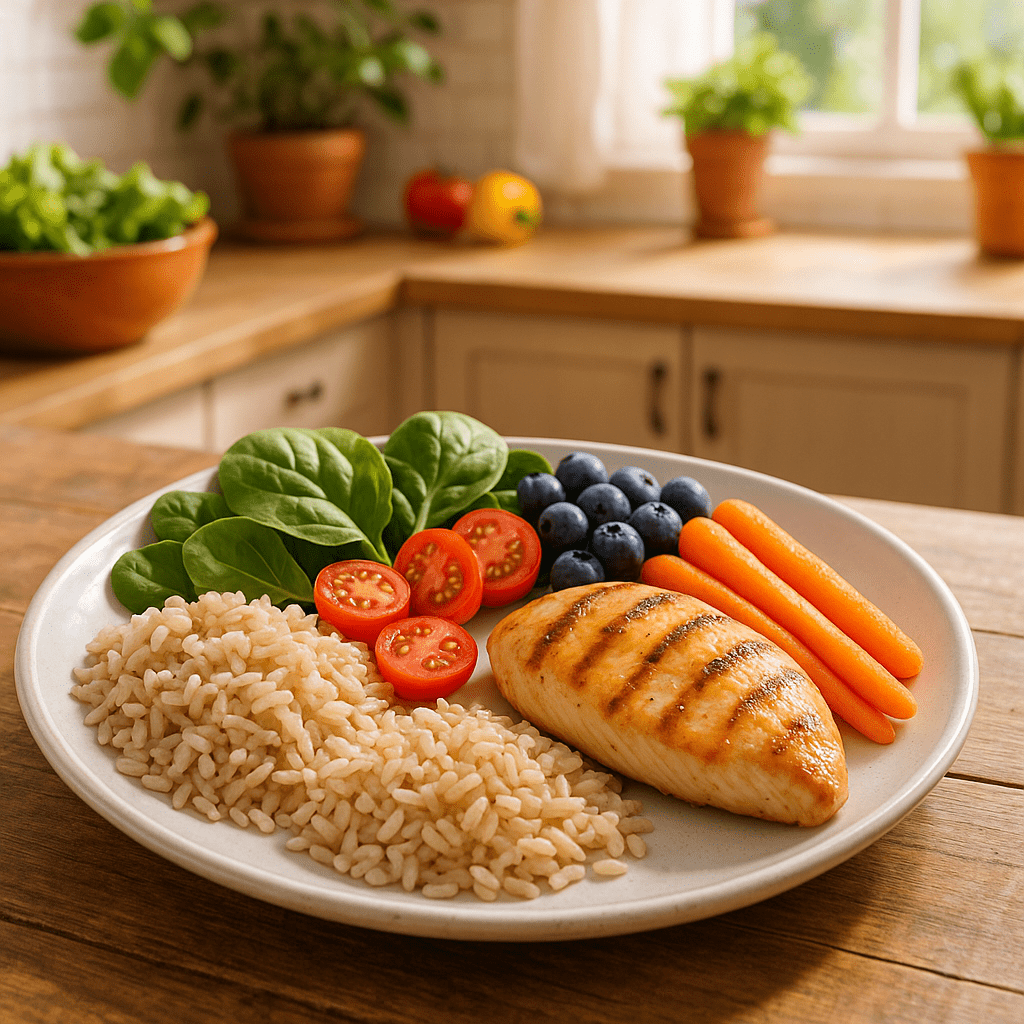
Lunch (13:00-14:00):
- grilled vegetables (zucchini, eggplant, bell pepper) with grains (buckwheat, brown rice or bulgur)
- grilled or boiled protein source (chicken
- breast, fish, tofu or chickpeas)
- fresh salad with olive oil and lemon juice
- glass of water or unsweetened tea
Supper (16:00-17:00):
- small bowl of cottage cheese with fresh fruit
- or hummus spread with carrot and cucumber sticks
Dinner (18:00-19:00):
- vegetable soup with whole grain bread
- small portion of protein (egg, fish, lentils)
- fresh vegetable salad with olive oil
- glass of water or herbal tea
- Between main meals, it is recommended to drink enough water – at least 1.5-2 liters per day. Water can be flavored with lemon,
- cucumber, or mint if plain water seems boring.
This diet plan is only a guideline and can be adjusted according to individual needs, food intolerances, or allergies. The most important thing is to maintain a balance of nutrients and eating regimen.
Recent research shows that a holistic approach to health, including proper nutrition and supplements, can maximize overall well-being and quality of life.
Conclusions
A balanced diet is the cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle that has a direct impact on our physical and emotional well-being. As we have seen, it is not a complicated or temporary diet, but rather a lifestyle based on a balance of various nutrients and conscious daily decisions.
The right ratio of protein, fat, carbohydrates and fiber, regular eating habits, appropriate portion sizes and the choice of healthy products – these principles allow our body to function optimally, maintain energy levels and protect ourselves from many chronic diseases.
It is important to understand that health is built every day, over a long period of time. There are no magic solutions or quick results – only consistent work and conscious choices. Start with small steps, try the daily diet plan provided and gradually form new habits.
If you have specific health problems, digestive disorders or dietary restrictions, it is always recommended to consult a doctor or nutritionist who will help you create an individual diet plan that meets your needs.
Remember – a balanced diet is an investment in yourself that will pay off in the long run in the form of better health, higher energy levels and a better quality of life. Food is not only fuel, but also medicine – let’s learn to use it wisely.
FAQ
What is a “balanced diet” and why is it important?
A balanced diet is a way of eating that ensures you get all the nutrients you need in the right proportions. It is important because it helps prevent nutrient deficiencies, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
What foods should I prioritize for a balanced diet?
Prioritize a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean protein sources (fish, poultry, legumes, nuts), and healthy fats. Include dairy products or dairy alternatives in your diet for calcium.
How can you control portion sizes without counting calories?
Use hand-sized guidelines: palm for protein, fist for vegetables or grains, thumb for fat. Use smaller plates, eat at regular intervals, and listen to your hunger/satiety signals.
Can a vegetarian diet be balanced and healthy?
Yes, a well-planned vegetarian diet can be completely balanced. It is important to include a variety of protein sources (beans, lentils, soy, nuts) and, if necessary, supplement the diet with iron or vitamin B12.
What are some easy ways to start and maintain healthy eating habits?
Start with small, actionable changes – plan meals in advance, always have healthy snacks on hand, and allow yourself to indulge in your favorite treats without guilt.