Potassium is an essential mineral for our body, responsible for muscle and nerve function, fluid balance, and blood pressure regulation. This vital trace element helps maintain heart rhythm, participates in protein synthesis, and ensures proper muscle contraction. Unfortunately, many people do not get enough potassium from their diet, which can have negative health consequences – from high blood pressure to muscle weakness. Athletes with hypertension and cardiovascular diseases should pay special attention to the amount of potassium in their diet. In this article, we will discuss seven foods that will help ensure sufficient potassium in the body.
By reading this article, you will learn not only which foods are high in potassium, but also how to properly prepare them and include them in your daily diet to get maximum benefits for heart health and overall well-being.
Why is potassium important for your health
Potassium is a mineral from the electrolyte group that is essential for the normal functioning of the body. It performs many vital functions, thanks to which our body remains healthy and functions properly.
One of the most important roles of potassium is blood pressure regulation. Scientific studies show that adequate potassium intake helps lower blood pressure and protects against hypertension. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that adults get at least 3,510 mg of potassium daily to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
In addition, potassium is responsible for the proper transmission of nerve signals and muscle contraction. When this mineral is lacking, you can feel muscle weakness, cramps or even heart rhythm disorders. Potassium also helps regulate fluid balance in the body, prevents the formation of edema (swelling) and contributes to bone strengthening.
Recent studies have revealed that adequate potassium intake can reduce the risk of stroke by as much as 24%. Specialists from the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences emphasize that adequate potassium intake is particularly important for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases, which is especially relevant in Lithuania, where these diseases remain one of the leading causes of death.
Potassium and heart disease prevention
Scientists have found that potassium helps reduce the effect of sodium on blood pressure. Sodium increases blood pressure, while potassium has the opposite effect – it lowers it. Therefore, a balanced ratio of these two minerals is particularly important for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
According to studies conducted in Europe, people whose diets are rich in potassium have a 20% lower risk of developing heart disease. Potassium deficiency can cause heart rhythm disorders, fatigue and muscle weakness. The benefits of chlorella for the body are also associated with the abundance of potassium and other minerals – this type of algae is an excellent additional source of potassium for vegetarians and vegans.
7 foods rich in potassium
When choosing foods rich in potassium, it is important to pay attention not only to the amount of potassium, but also to the overall nutritional value of the product and its availability in the daily Lithuanian diet. These seven products are distinguished not only by their high potassium content, but also by other properties beneficial to the body.
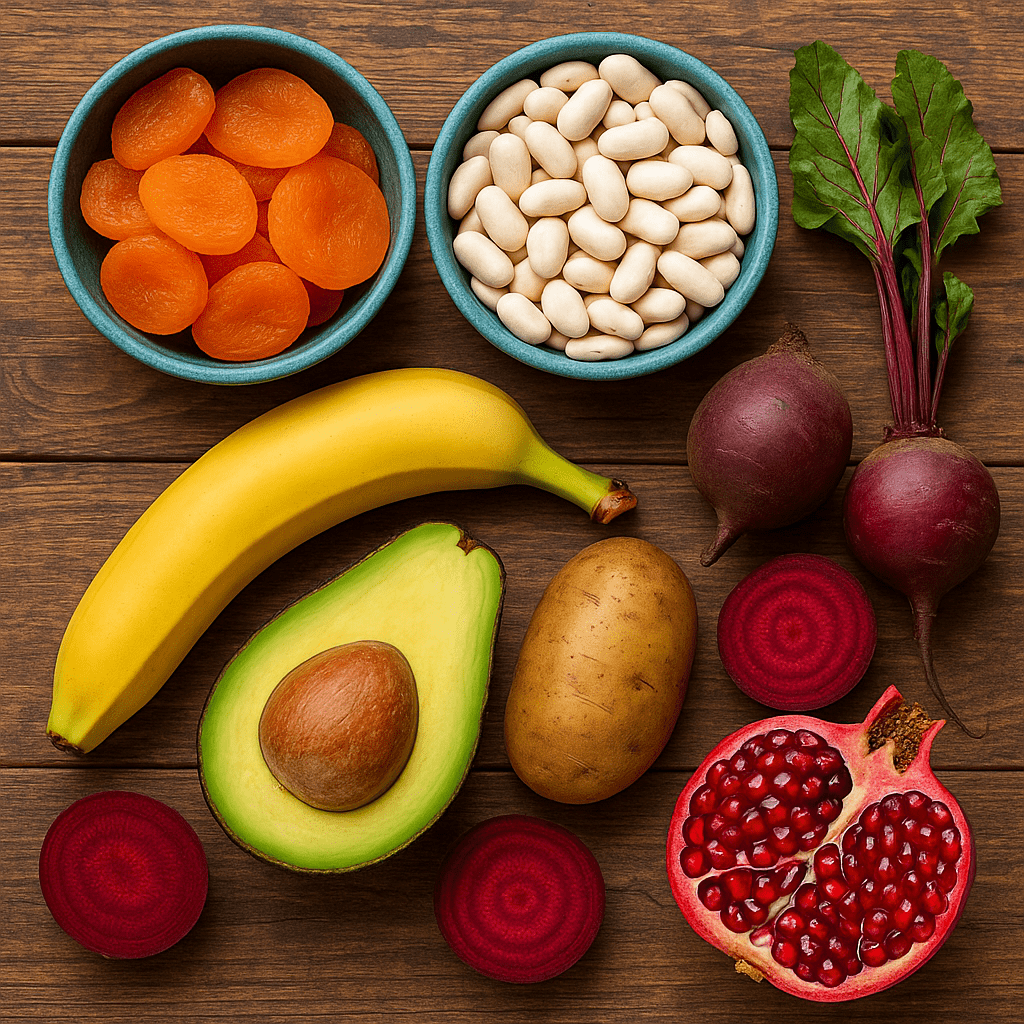
1. Dried Fruit
Dried fruit, especially apricots, prunes, and raisins, are a real treasure trove of potassium
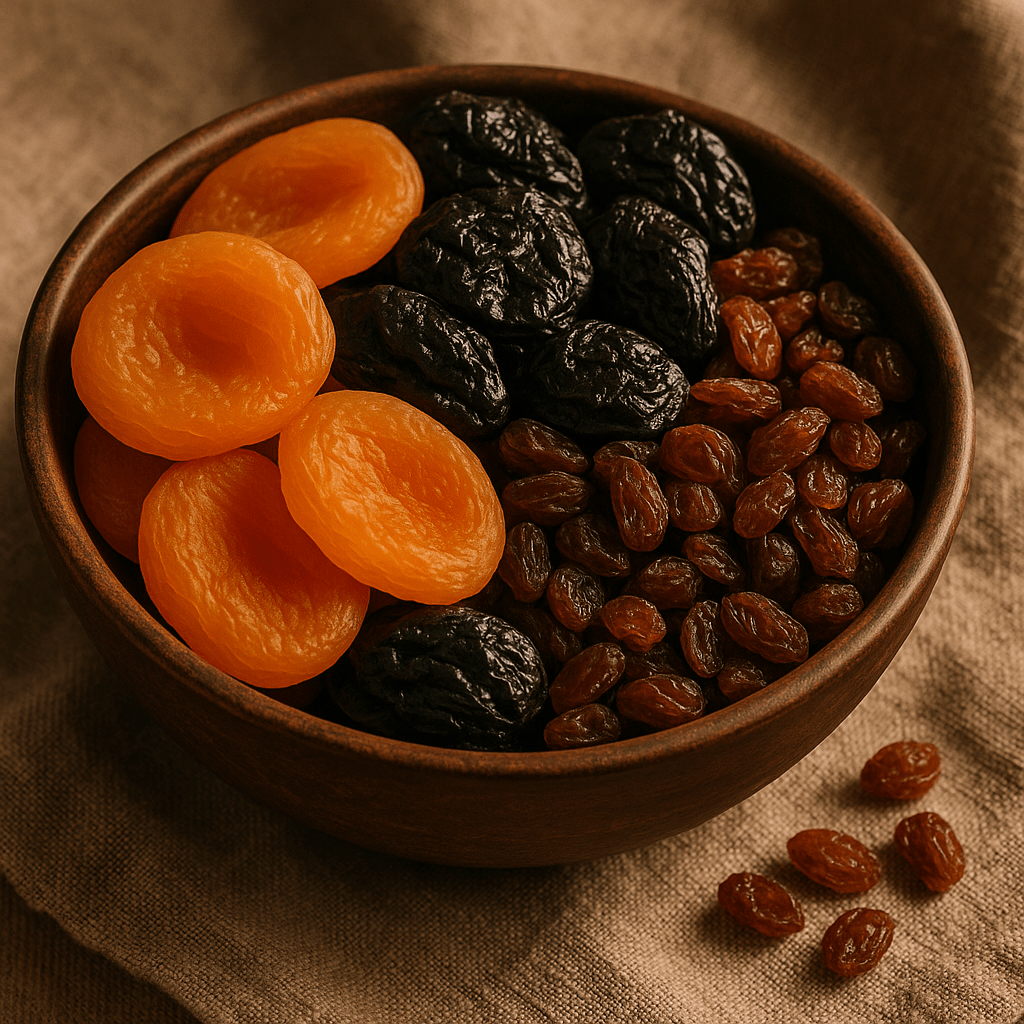

100 g of dried apricots contain about 1850 mg of potassium, which is almost 70% of the recommended daily allowance. Dried fruits are a concentrated source of nutrients that are perfect as a snack between main meals.
Dried apricots are especially valued for their high potassium content and antioxidants. They not only provide the body with potassium, but also with other valuable substances – beta-carotene, iron and fiber. Dried plums are also high in potassium and have a positive effect on digestion.
Tip: Dried fruits are especially suitable for older people and athletes, but you should pay attention to the calorie and sugar content – consume them in moderation, especially if you have problems with blood sugar regulation.
2. White beans
White beans are distinguished by an extremely high potassium content – 100 g of the product contains from 1000 to 1300 mg of potassium. They are also a great source of protein, fiber, and other minerals. Regular consumption of legumes has been linked to a lower risk of heart disease and better gut health.
White beans have a low glycemic index, making them suitable for diabetics and those looking to control their weight. They are also rich in folate, magnesium, and iron, which, together with potassium, form a valuable mineral complex.
Tip: When preparing beans, soak them overnight and change the water before cooking to reduce the amount of gas-causing substances in the intestines.
3. Bananas
Bananas are often cited as one of the most popular sources of potassium. A medium-sized banana (about 118 g) contains about 420 mg of potassium. Although this is less than in other foods on the list, bananas are distinguished by their excellent bioavailability of potassium and convenience – they are easy to include in your daily diet.
Compared to other fruits, bananas are exceptionally high in potassium. They also provide the body with vitamin B6, vitamin C and fiber. Bananas are especially popular with athletes because of their fast-absorbing carbohydrates and electrolytes, which help restore strength after training.
4. Avocados
Half of a medium-sized avocado (about 100 g) provides about 485 mg of potassium, which is about 10% of the recommended daily intake. Avocados are also rich in healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants.
Avocados are unique in that their potassium pairs well with monounsaturated fats, which help support heart health. Studies show that regular avocado consumption is associated with better cholesterol levels and a lower risk of heart disease.
Tip: Adding avocado oil to salads or other dishes can improve the absorption of vitamins and minerals from other vegetables.
Tip: Choose slightly unripe bananas if you want less sugar, or very ripe ones with brown spots if you want more antioxidants.
5. Potatoes
Potatoes are the basis of Lithuanian cuisine and an excellent source of potassium. A medium-sized baked potato with its skin (about 173 g) provides about 900 mg of potassium. It is important to note that most of the potassium is found closer to the skin, so it is best to bake or boil potatoes with their skin.
Potatoes are often unjustifiably considered a junk food, but they are rich not only in potassium, but also in vitamins C, B6 and fiber. In addition, they are low in calories (if not prepared with a lot of fat), so they are suitable for a variety of diets.
Tip: To preserve the most potassium and other nutrients, it is best to bake potatoes in the oven with their skin on or steam them. This way you will preserve up to 50% more minerals than boiling them in water.
Vitamins for joints and bones are also important for maintaining health, especially if your diet is deficient in minerals and vitamins.
6. Beetroot
Beetroot is a traditional Lithuanian vegetable, rich not only in potassium (100 g of the product contains about 325 mg), but also in other valuable substances. They are characterized by natural nitrates, which improve blood circulation and lower blood pressure.
Beetroot is distinguished by the fact that it can be consumed both cooked and raw. The antioxidants it contains help fight inflammatory processes in the body and improve physical performance. Studies show that regular consumption of beetroot juice can improve endurance and sports performance.
Tip: You can add grated raw beetroot to salads, and serve baked in the oven as a side dish. This way you will preserve more valuable substances than when boiling.
7. Pomegranates
Pomegranates are a real superfood, rich in potassium (about 235 mg per 100 g of fruit seeds) and other valuable substances. They have strong antioxidant properties and a positive effect on the cardiovascular system.
Pomegranate juice and seeds help reduce blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels and protect against atherosclerosis. Pomegranate antioxidants are also associated with better kidney function, which is especially important for potassium metabolism in the body.
Tip: You can add pomegranate seeds to yogurt, porridge or salads. Remember that pomegranate juice contains a lot of sugar, so it is better to choose the seeds themselves, rather than industrially produced juice.
Other Valuable Sources of Potassium
In addition to the seven main sources of potassium mentioned above, it is worth mentioning other foods that are also rich in this valuable mineral:
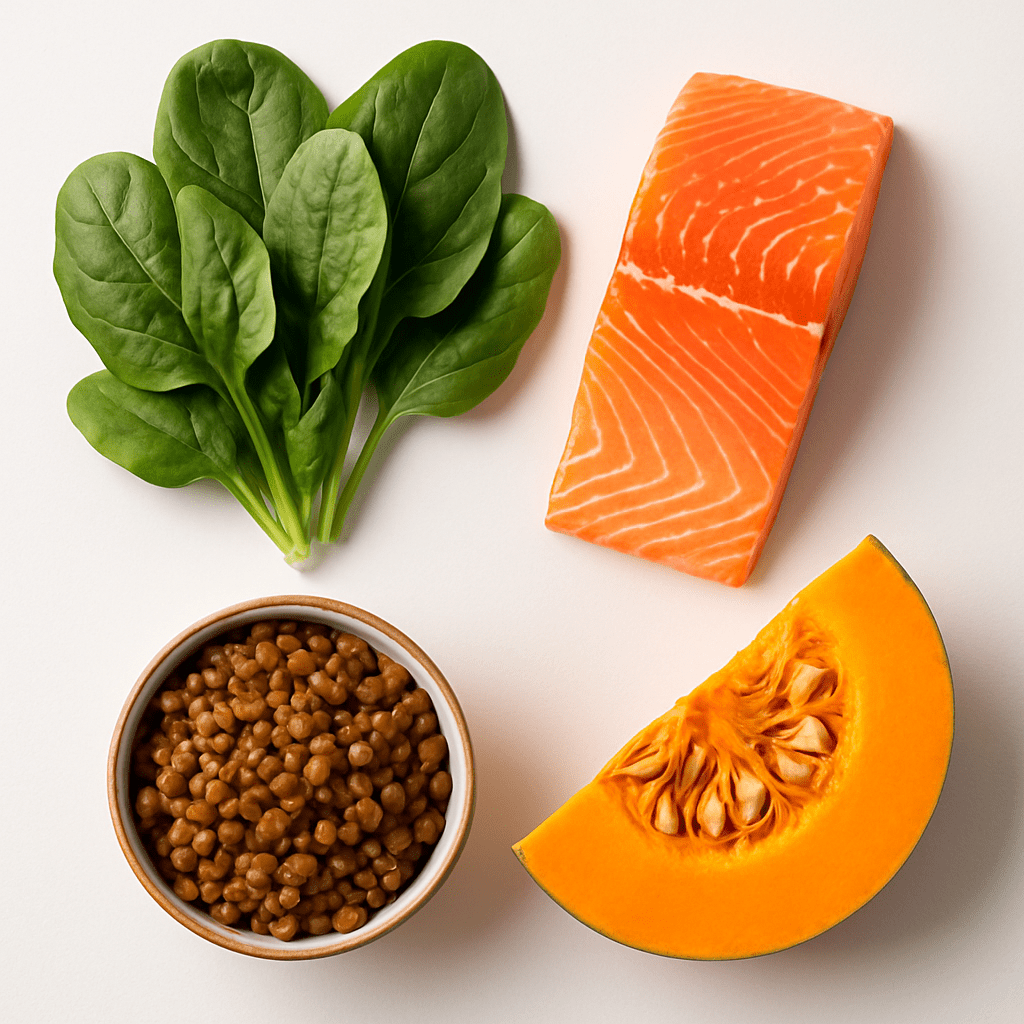
- Spinach (558 mg potassium per 100 g)
- Lentils (369 mg potassium per 100 g of cooked lentils)
- Salmon (414 mg potassium per 100 g)
- Pumpkin (230 mg potassium per 100 g)
These products will not only supplement your diet with potassium, but also with other valuable nutrients, vitamins and minerals.

Berberine improves metabolism and helps maintain optimal potassium levels, especially for those who have difficulty getting enough potassium from their diet.
How to Maximize Potassium Naturally
To get the most out of potassium-rich foods, it’s important to know how to properly prepare and combine them. Studies show that the way food is processed can have a significant impact on the amount of potassium and other minerals in the final dish.
One of the main principles is to try to consume as few processed foods as possible. Processing often removes some of the valuable minerals, including potassium. Fresh or minimally processed vegetables and fruits tend to have the most potassium.
The way you cook your food also affects potassium levels. When you boil food in water, some of the potassium is lost to the water, so this cooking method is not the best. Steaming, baking, or braising preserves more potassium and other minerals.
- Steaming is one of the best ways to preserve potassium in vegetables.
- Baking in the oven is great for potatoes, beets, and other potassium-rich foods.
- Cooking foods with the skin on (e.g., potatoes, apples) helps preserve more minerals.
- Food combination – combine potassium-rich foods with healthy fats (e.g., avocado, olive oil), which improves mineral absorption.
It is also important to pay attention to the information provided on food labels. Although the amount of potassium is not always indicated in Lithuania, higher-quality products often have more detailed information about nutritional value. Choose natural, less processed products with less added sodium – this will help maintain the right balance of sodium and potassium.
Who should be careful – excess potassium and special diets
While adequate potassium intake is beneficial and even necessary for most people, certain groups should carefully monitor their potassium intake. Excess potassium, called hyperkalemia, can be dangerous, especially for those with certain health problems.
Monitoring potassium levels is especially important for people with chronic kidney disease. Healthy kidneys are efficient at removing excess potassium from the body, but kidney disease impairs this process. In this case, excessive potassium levels can cause serious complications, including heart rhythm disorders.
Patients taking certain medications should also pay attention to their potassium intake. Some medications for hypertension, heart failure, or anti-inflammatory medications can increase potassium levels in the blood. These people are advised to consult a doctor about the appropriate amount of potassium in their diet.
People with diabetes should also carefully monitor their potassium intake, as insulin deficiency or resistance can affect the distribution of potassium in the body. In addition, diabetic neuropathy can impair kidney function, which further complicates potassium metabolism.
Symptoms of a potassium deficiency can include muscle weakness, cramps, fatigue, and high blood pressure. Symptoms of an excess include heart rhythm disturbances, weakness, and numbness. In both cases, it is important to consult a doctor, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
If you are at risk, it is recommended that you work with your doctor to create an individualized diet plan that meets your health needs and helps prevent potential complications.
Summary
Potassium is a vital mineral that is essential for the normal functioning of the body. Adequate intake of potassium in the diet helps maintain normal blood pressure, strengthen the heart, and ensure proper functioning of the muscles and nervous system.
The richest sources of potassium are dried fruits, white beans, bananas, avocados, potatoes, beets, and pomegranates. These products not only provide the body with potassium, but also other valuable nutrients that contribute to improving overall health.
It is important to remember that the method of preparation of food affects the amount of potassium in the final dish. Try to choose steaming, baking, or stewing, which will preserve more valuable minerals. It is also worth noting that some groups of people, especially those with kidney problems or taking certain medications, should carefully monitor their potassium intake.
A balanced, varied diet rich in fresh fruits, vegetables, legumes, and other whole foods is the best way to ensure optimal potassium levels. It is always a good idea to consult a healthcare professional for individual dietary recommendations, especially if you have specific health concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which foods are high in potassium?
Dried fruits, especially apricots, and white beans are some of the richest sources of potassium—one serving can provide up to 70% of your daily potassium requirement.
How much potassium do I need each day?
Most adults are recommended to consume 3,500-4,000 mg of potassium per day, but individual needs may vary; always consult your healthcare professional.
Can potassium help lower blood pressure?
Yes—regular potassium intake helps control blood pressure, especially when combined with reducing sodium intake.
Are bananas really the best source of potassium?
While bananas are known for their potassium content, foods like beans, dried fruits, and potatoes actually have more potassium per serving.
Should everyone eat foods high in potassium?
Most people benefit from potassium-rich foods, but those with kidney, heart, or certain metabolic conditions should watch their potassium intake carefully.

